Shingles is usually assumed as a once-in-a-lifetime experience. But wait! Shingles can definitely come again, even among healthy adults. However, it’s just unlikely. The shingles virus, herpes zoster can come back a second and seldom, a third time.
Experts are not sure exactly how many people get the disease more than once. But they know it is likely to come back in people with weak immune systems.

How frequently would Shingles return?
A study observed at medical records from about 1700 patients aged more than 22 who had shingles. The study then examined over their second episode. They discovered that the reappearance rate was more than 5%, similar to having the first occurrence of shingles. Some people had experienced several episodes. The average follow-up was only eight years. Thus, the actual reappearance rate is most likely above 5%, says author of the research Dr. Barbara Yawn.
What causes shingles to reoccur?
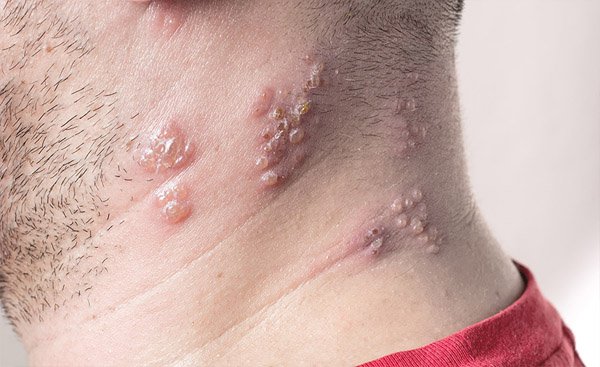
Shingles, caused by Varicella Zoster Virus, strikes only people who had chicken pox in the past. The virus actually never leaves the patient’s body completely and can remain inactive for years in the nerve roots in the spinal column, until it abruptly reproduces and starts the movement down the nerves to cause the disease.
What exactly triggers the virus to stir is still unidentified, research is underway to determine. However, it appears to occur when the immune system is weakened brought on by aging, illness, transplant recipients and people with cancer (especially those going through chemotherapy). Some theories suggest that stress may also cause shingles outbreak.
Some people with shingles get minor rash lasting for few days, while others develop a severe nerve pain, making the affected area more sensitive. Dr. Yawn says that sometimes patients can’t even stand to have anything touch the affected area, not even clothes. If shingles occurs at the second time, usually it doesn’t appear in the same location.
Who is more expected to get Shingles again?
You are likely to get shingles back in the following instances:
- Women: Women are more likely to contract shingles than men and also a recurrence.
- Compromised immune system: Your immune system is weak from conditions such as HIV, leukaemia or you are under medications which overpower your immune system.
- Old age: You are above 50 years or older when you had shingles the first time.
- PHN: You had severe pain which continued for more than a month after the initial onset of shingles, known as post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN). While antiviral medicines can reduce the time period and severity of shingles, PHN is difficult to treat.
Will the shingles vaccine help?

The vaccine for shingle, Zostavax doesn’t abolish all cases. However, research has shown that it can cut down the risk by about half in people with age 60 or above. The episodes occurring in vaccinated people are likely to be milder.
Unlike most vaccines, whose key purpose is to ward off a virus for the first time it occurs, Zostavax improves the immune system’s capability to keep the virus in check, although it never completely disappears. Although the effectiveness of vaccine in preventing reoccurrence of virus has not been confirmed in clinical studies.
Zostavax, FDA approved vaccine, is one of the most expensive vaccines and ranges from $140 to $400. Usually, it’s side effects are limited to mild itching and sensitivity around the injection site. Not all Medicare Part D plans cover this vaccine. The availability of this vaccine can be checked at www.zostavax.com.
The Centers for Disease Control has advised all Americans aged 60 or above to get vaccine for shingles – whether they’ve had it before or not. People should not wait to get very old to get vaccines. With weak immune system, you would no longer be eligible to get this vaccine because of increased risk to get shingles instead of preventing it.
