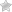Most often, shingles affects children over 10 years of age. Patients who had been previously infected with chickenpox are at special risk. The disease manifests itself on the body by specific rashes in sensitive areas. The infection can spread after direct contact with sick person. The disease might be complicated by other diseases which will lead to new symptoms.
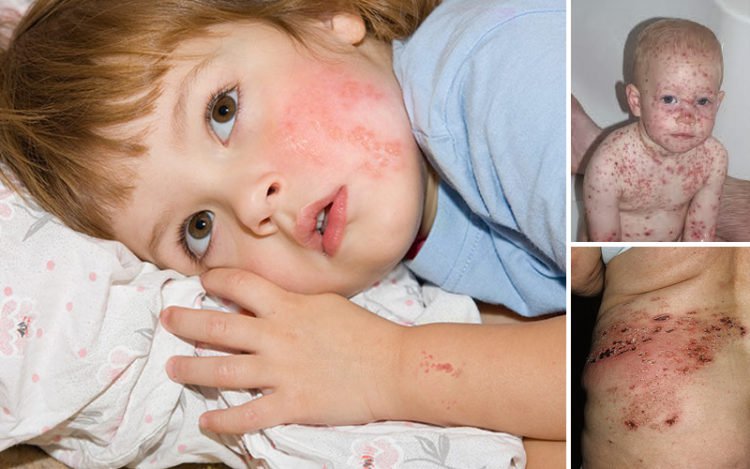
Symptoms
Children experience more severe symptoms of the disease than adult patients. Person experiences a sharp rise in body temperature, itching and burning at the location of the rash. Pain and unpleasant stinging sensations might be felt near the nerves affected by shingles. There is a high probability of general malaise and physical weakness.
At the second stage of the disease the affected areas of the skin turn red and become denser, and then edema with distinctive papules appear. Infectious nodules can quickly develop and spread to the nearest parts of the skin. The formations have inflammations and a transparent liquid inside. The knots are crusted after the first week.
Among those who face the biggest risk are teenagers, immunocompromised patients, premature infants, newborns from mothers who have previously suffered varicella.
Diagnosis
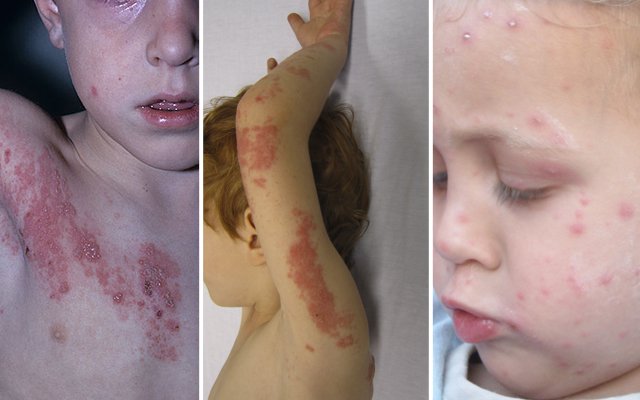
Inflamed nodules with a transparent liquid are the first sign of shingles. In the first stages, red dense areas of the skin can be noticed. Diagnosis of shingles is similar to the diagnosis of chicken pox. Medical tests are carried out in laboratory.
Treatment
If distinctive nodules appear on the skin, a complex treatment is used which includes the following methods:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy treatment.
Analgesics and salicylates are used as prescribed drugs. In severe cases of the disease development, depending on the child’s health, physicians prescribe intravenous antiviral drugs.
The effectiveness of vaccination is not proven, but in severe cases of the disease or with repeated relapses, immunoglobulin might be used.